How Long Does It Take for Blood to Circulate?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding blood circulation, an essential process in the human body, is crucial. It helps deliver nutrients and oxygen to cells while removing waste products. But how long does it actually take for blood to circulate through the entire body? This is a question that many people might not immediately think about, but it plays a significant role in understanding how our bodies function and maintain their various processes.
In this article, we will explore the process of blood circulation, how long it takes for blood to travel through the body, factors that can affect circulation time, and how you can promote healthy circulation.
What is Blood Circulation?
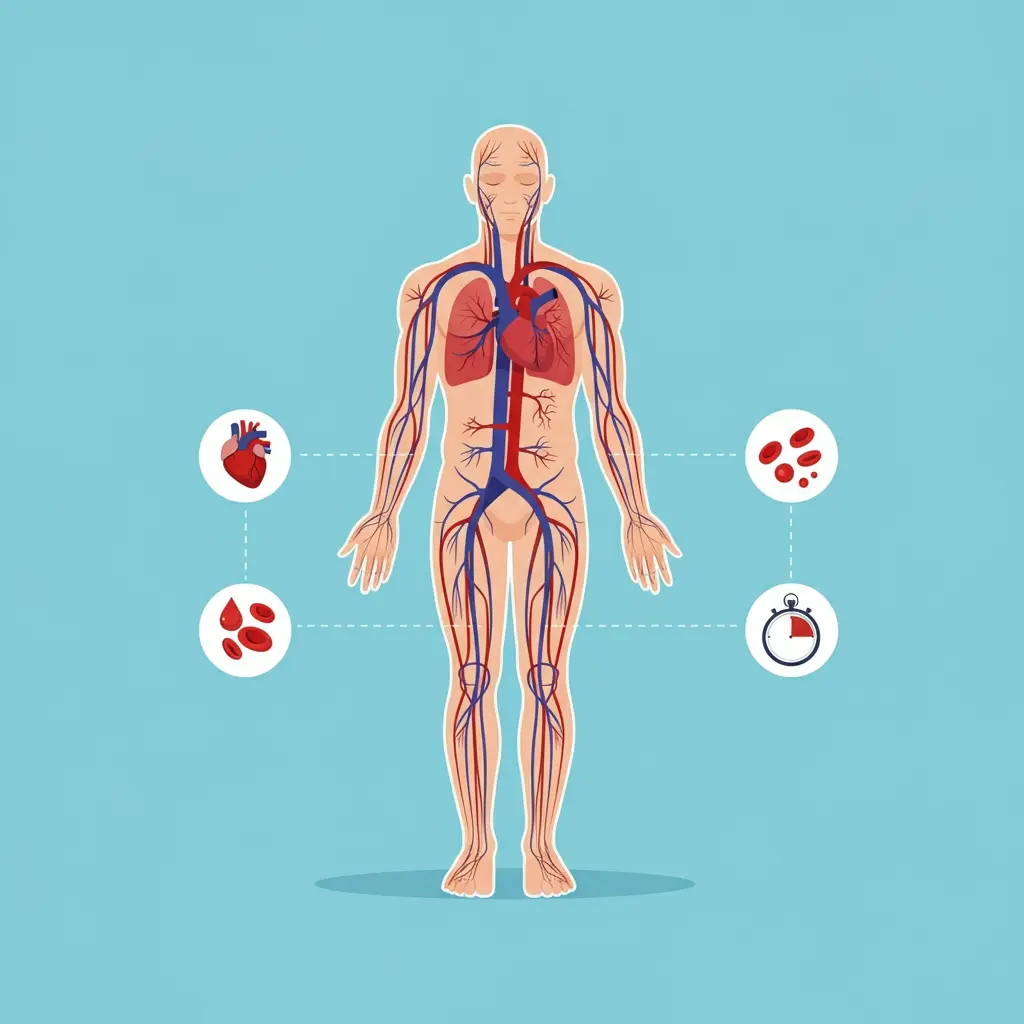
Blood circulation refers to the continuous movement of blood throughout the body, which is powered by the heart. This process allows the delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and other vital substances to tissues and organs, while also carrying waste products like carbon dioxide and urea away from the cells for excretion.
The circulatory system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. It’s a highly organised system that ensures all parts of the body receive the essential components they need for proper function.
How the Circulatory System Works
To better understand how long blood takes to circulate, it’s important to know how the circulatory system operates.
The Heart: The Engine of Circulation
The heart, a marvel of biological engineering, is the central organ that drives blood circulation. It pumps oxygenated blood through the body via the arteries and returns deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the veins. The heart works as a pump, and its beat helps keep the blood moving throughout the vascular system.
The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, while the left side pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body. The heart beats approximately 70-75 times per minute in a resting adult, which means it pumps blood through the body many times each minute.
Blood Vessels: Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries
Blood vessels carry blood throughout the body. The three main types are:
- Arteries: These blood vessels carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to various tissues and organs. The main artery, called the aorta, branches into smaller arteries as it moves away from the heart.
- Veins: These vessels return deoxygenated blood to the heart. Veins have valves that prevent blood from flowing backwards.
- Capillaries: These are the smallest blood vessels, where the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products occurs between blood and tissues.
The Role of Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, play a crucial role in transporting oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and returning carbon dioxide to the lungs to be expelled. These cells are the most numerous type of blood cell and are designed to efficiently carry oxygen due to their biconcave shape, which increases their surface area. They are produced in the bone marrow and have a lifespan of about 120 days, after which they are removed from the circulation by the spleen and liver.
The Time It Takes for Blood to Circulate
The time it takes for blood to circulate throughout the entire body is generally referred to as the ‘circulation time.’ In simpler terms, it is the duration it takes for blood to travel from the heart, through all the major organs and tissues, and return to the heart.
Average Time for Blood to Circulate Through the Body
On average, it takes about one minute for blood to complete one full circulation cycle, from being pumped by the heart, through the arteries, into the veins, and back to the heart. However, this time can vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the body and the health of the circulatory system.
Factors Affecting Blood Circulation Time
Several factors can influence how long it takes for blood to circulate:
- Heart Rate: The faster your heart beats, the quicker blood is pumped through your body. A higher heart rate means faster circulation.
- Physical Activity: During exercise, your heart rate increases, which can speed up circulation time. Your body demands more oxygen and nutrients, and the heart works harder to supply them.
- Age: As you age, the elasticity of your blood vessels may decrease, and your heart may not pump as efficiently, slowing down circulation.
- Health Conditions: Conditions such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), or other cardiovascular diseases can affect circulation, making it slower or less efficient.
- Blood Vessel Condition: If your blood vessels are dilated (widened), blood may circulate faster, while constricted blood vessels can slow circulation.
Blood Circulation and Your Health
Good circulation is crucial for overall health. When blood flows properly throughout the body, it ensures that your organs and tissues receive the oxygen and nutrients they need, and waste products are removed. Poor circulation can lead to numerous health problems, such as fatigue, cold extremities, and even more serious issues like heart attacks or strokes.
Impact of Blood Circulation on Body Function
Blood circulation impacts many of the body’s key functions, such as:
- Oxygen Transport: Blood carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs throughout the body. Without adequate circulation, oxygen can’t be delivered efficiently, which can result in fatigue, dizziness, and weakness.
- Nutrient Delivery: Blood also carries nutrients like glucose, vitamins, and minerals to cells, ensuring they have the energy and building blocks needed for repair and growth.
- Waste Removal: Blood helps transport waste products, including carbon dioxide, to the lungs for exhalation and urea to the kidneys for elimination.
How Fast Does Blood Flow?
Blood does not flow at a constant speed throughout the body. The speed of blood flow depends on the type of blood vessel and the region of the body.
Average Blood Flow Speed in Different Vessels
- Arteries: Blood moves fastest in the arteries, with speeds reaching up to 1 meter per second. This is because arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart under higher pressure.
- Capillaries: Blood flow slows significantly in the capillaries. Capillaries are tiny vessels where oxygen and nutrient exchange occur, so blood must move slowly to allow for this process. The speed here can drop to just a few millimetres per second.
- Veins: Blood moves more slowly in veins compared to arteries, with an average speed of about 0.2 meters per second. This is due to the lower pressure in veins and the need to return blood to the heart.
Effects of Exercise on Blood Flow
When you exercise, your heart rate increases, causing blood to circulate faster to meet the oxygen demands of your muscles. In fact, during intense physical activity, blood flow to your muscles can increase by up to 10 times to supply more oxygen and nutrients.
The Importance of Proper Circulation
Proper circulation is crucial for maintaining health. Without it, your body’s cells would be deprived of oxygen and nutrients, and waste products would build up. Several conditions can result from poor circulation, including:
- Cold Hands and Feet: Poor circulation can cause blood to have trouble reaching extremities like your hands and feet, leading to a feeling of coldness or numbness.
- Varicose Veins: When blood flow becomes sluggish in veins, it can cause blood to pool and form varicose veins, which are swollen, twisted veins visible under the skin.
- Fatigue: Without proper circulation, your body’s organs and tissues may not get the oxygen they need, leading to tiredness and lack of energy.
Poor Circulation: Causes and Risks
Several factors can contribute to poor circulation:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of fatty deposits on the walls of arteries can restrict blood flow.
- Blood Clots: Clots can block blood vessels, leading to reduced circulation and even more serious complications like strokes.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put pressure on blood vessels, affecting circulation.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow efficiently.
How to Improve Circulation
To improve circulation, consider these tips:
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity strengthens the heart and improves blood flow.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fibre can help improve circulation.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain optimal blood flow.
- Avoid Smoking: Quitting smoking can significantly improve circulation by keeping blood vessels healthy.
- Elevate Legs: Elevating your legs periodically can help improve circulation, especially if you spend a lot of time sitting or standing.
Common Questions About Blood Circulation
How long does it take blood to travel from the heart to the brain?
Blood takes just a few seconds to travel from the heart to the brain, as the brain is supplied by arteries directly branching off from the aorta.
Does blood circulation time vary by age?
Yes, blood circulation tends to slow as you age due to changes in the elasticity of blood vessels and a decrease in heart efficiency.
How does blood circulation change during exercise?
Exercise increases heart rate and blood flow, allowing oxygen and nutrients to reach muscles more efficiently.
Can blood circulate faster with good health?
Yes, regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking can improve circulation speed and efficiency.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Circulation
To maintain good circulation:
- Exercise regularly to keep your heart and blood vessels in good condition.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated and avoid prolonged sitting or standing.
- Wear compression stockings if you’re prone to varicose veins.
Final Thoughts
The time it takes for blood to circulate through your body is generally quite short, with an average cycle taking just around one minute. However, the efficiency and speed of circulation can vary depending on factors like exercise, age, and overall health. Understanding how your circulatory system works and maintaining good circulation can have a significant impact on your overall well-being. Regular exercise, healthy eating habits, and avoiding harmful practices like smoking are essential for keeping your blood flowing smoothly throughout your life.